Scientists use DNA analysis to gain insights into species evolution by comparing genome sequences of different organisms. These comparisons are then organized into a phylogenetic tree which shows evolutionary relationships. Hence, the answer is By signing up, you accept Quizlet’s ISBN: 9780132013499Kenneth R. Miller, Levine
Forensic Biology: Science Gets Criminal
DNA methylation. Two main experimental methods have been applied to map DNA methylation signatures on ancient genomes. The first builds on methods commonly used on fresh DNA, such as bisulfite
Source Image: jgi.doe.gov
Download Image
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is the blueprint for all inherited characteristics in living things. It is a very long sequence, written in code, that needs to be transcribed and translated before a cell can make the proteins that are essential for life.
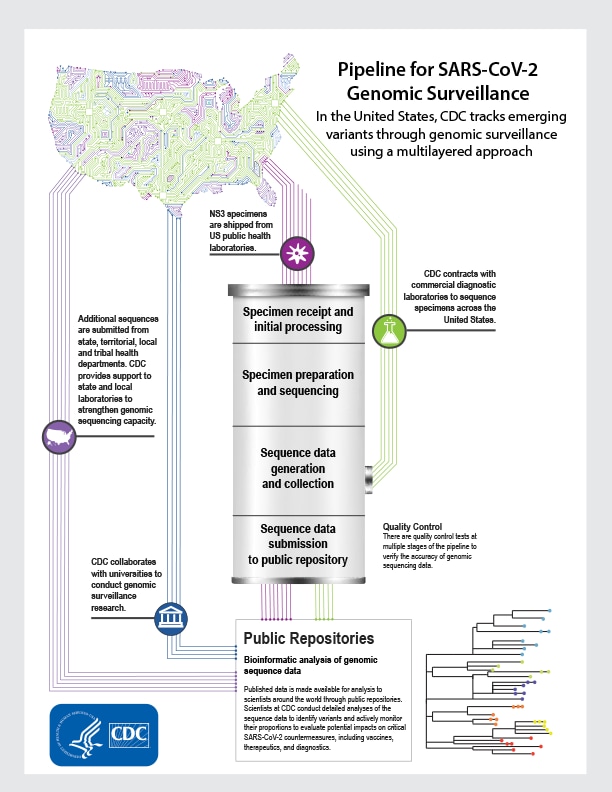
Source Image: cdc.gov
Download Image
Decoding Humanity: How Mapping the Mouse Brain Unveils Human Secrets by the Understanding Evolution team A mutation is a change in DNA, the hereditary material of life. An organism’s DNA affects how it looks, how it behaves, and its physiology. So a change in an organism’s DNA can cause changes in all aspects of its life. Mutations are essential to evolution; they are the raw material.

Source Image: sciencenews.org
Download Image
How Does Dna Analysis Help Scientists Better Understand Evolution
by the Understanding Evolution team A mutation is a change in DNA, the hereditary material of life. An organism’s DNA affects how it looks, how it behaves, and its physiology. So a change in an organism’s DNA can cause changes in all aspects of its life. Mutations are essential to evolution; they are the raw material. Being able to sequence ancient DNA provides a snapshot of those people at a specific point in time. Extracting this DNA starts by finding the right kinds of bones, like teeth or the small, dense bones of the inner ear (petrous bone), that preserve enough DNA inside. Researchers then grind a section or drill into the bone and prepare the
Here are 5 cool findings from a massive project on 240 mammal genomes
Build A Tree: Students build phylogenetic trees themed around the evidence of evolution, including fossils, biogeography, and similarities in DNA. Students use both morphology and analysis of The Colossal de-extinction plan | Popular Science

Source Image: popsci.com
Download Image
Learning Genetic Algorithm – An Evolutionary Algorithm Build A Tree: Students build phylogenetic trees themed around the evidence of evolution, including fossils, biogeography, and similarities in DNA. Students use both morphology and analysis of

Source Image: analytixlabs.co.in
Download Image
Forensic Biology: Science Gets Criminal Scientists use DNA analysis to gain insights into species evolution by comparing genome sequences of different organisms. These comparisons are then organized into a phylogenetic tree which shows evolutionary relationships. Hence, the answer is By signing up, you accept Quizlet’s ISBN: 9780132013499Kenneth R. Miller, Levine
Source Image: wardsworld.wardsci.com
Download Image
Decoding Humanity: How Mapping the Mouse Brain Unveils Human Secrets Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is the blueprint for all inherited characteristics in living things. It is a very long sequence, written in code, that needs to be transcribed and translated before a cell can make the proteins that are essential for life.

Source Image: scitechdaily.com
Download Image
Mind Mapping: A Human Brain Cell Atlas Ushering In “A New Era in Brain Science” News update, July 2021. More than a decade ago, the existence of Denisovans was discovered based on DNA extracted from a bone found in a Siberian cave. In the years since, scientists have found more traces of Denisovan DNA — in the Neanderthal and modern human genomes, as well as in remains from that same cave.

Source Image: scitechdaily.com
Download Image
Teach Genetics and Heredity with Free STEM Lessons & Activities – Genetics Science Projects | Science Buddies Blog by the Understanding Evolution team A mutation is a change in DNA, the hereditary material of life. An organism’s DNA affects how it looks, how it behaves, and its physiology. So a change in an organism’s DNA can cause changes in all aspects of its life. Mutations are essential to evolution; they are the raw material.

Source Image: sciencebuddies.org
Download Image
DNA Poster | Teaching biology, Gcse science, Teaching science Being able to sequence ancient DNA provides a snapshot of those people at a specific point in time. Extracting this DNA starts by finding the right kinds of bones, like teeth or the small, dense bones of the inner ear (petrous bone), that preserve enough DNA inside. Researchers then grind a section or drill into the bone and prepare the

Source Image: pinterest.com
Download Image
Learning Genetic Algorithm – An Evolutionary Algorithm
DNA Poster | Teaching biology, Gcse science, Teaching science DNA methylation. Two main experimental methods have been applied to map DNA methylation signatures on ancient genomes. The first builds on methods commonly used on fresh DNA, such as bisulfite
Decoding Humanity: How Mapping the Mouse Brain Unveils Human Secrets Teach Genetics and Heredity with Free STEM Lessons & Activities – Genetics Science Projects | Science Buddies Blog News update, July 2021. More than a decade ago, the existence of Denisovans was discovered based on DNA extracted from a bone found in a Siberian cave. In the years since, scientists have found more traces of Denisovan DNA — in the Neanderthal and modern human genomes, as well as in remains from that same cave.