Hint Check Answer < Question 11 of 15 > Attempt 2 The graphs illustrate an initial equilibrium for the economy. Suppose that unexpectedly good weather causes a much larger yield of corn crops than expected. Use the graphs to show the new positions of aggregate demand (AD), short-run aggregate supply (SRAS), and This problem has been solved!
Phillips Curve in the Short & Long Run | Definition & Graph – Lesson | Study.com
in a market setting, disequilibrium occurs when quantity supplied is not equal to the quantity demanded; when a market is experiencing a disequilibrium, there will be either a shortage or a surplus. equilibrium price. the price in a market at which the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied of a good are equal to one another; this is also
Source Image: coursehero.com
Download Image
In this example, our demand and supply model will illustrate the market for salmon in the year before the good weather conditions began—you can see it above. The demand curve D0 and the supply curve S0 show that the original equilibrium price was $3.25 per pound and the original equilibrium quantity was 250,000 fish. This price per
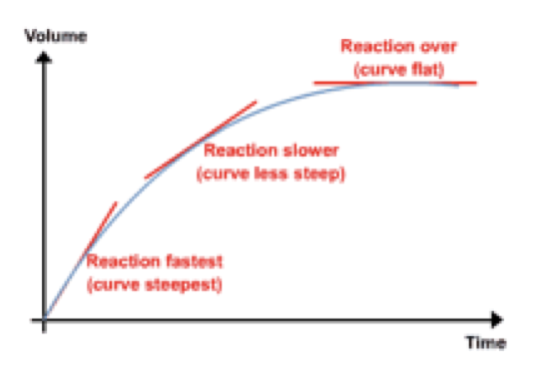
Source Image: studymind.co.uk
Download Image
Germany: Reaching net zero while safeguarding social cohesion – ECOSCOPE Next, consider how an economic change (e.g. a natural disaster, a change in production technology, a change in tastes and preferences, income, etc.) might affect supply or demand, then make adjustments to the graph to identify the new equilibrium point. Step 1. Draw demand and supply curves showing the market before the economic change took place.
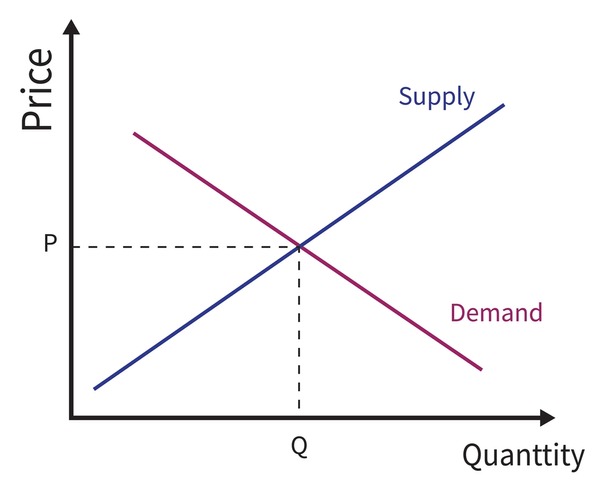
Source Image: shutterstock.com
Download Image
The Graphs Illustrate An Initial Equilibrium For Some Economy
Next, consider how an economic change (e.g. a natural disaster, a change in production technology, a change in tastes and preferences, income, etc.) might affect supply or demand, then make adjustments to the graph to identify the new equilibrium point. Step 1. Draw demand and supply curves showing the market before the economic change took place. A Decrease in Demand. Panel (b) of Figure 3.10 “Changes in Demand and Supply” shows that a decrease in demand shifts the demand curve to the left. The equilibrium price falls to $5 per pound. As the price falls to the new equilibrium level, the quantity supplied decreases to 20 million pounds of coffee per month.
Demand Curve Royalty-Free Images, Stock Photos & Pictures | Shutterstock
Social Science Economics Macroeconomics Ch. 12: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply Which of the statements best describes why the aggregate demand curve is downward sloping? An increase in the aggregate price level causes consumer and investment spending to fall, because consumer purchasing power decreases and money demand increases. Microeconomics Exam II Review Flashcards | Quizlet

Source Image: quizlet.com
Download Image
Demand Curve | INOMICS Social Science Economics Macroeconomics Ch. 12: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply Which of the statements best describes why the aggregate demand curve is downward sloping? An increase in the aggregate price level causes consumer and investment spending to fall, because consumer purchasing power decreases and money demand increases.
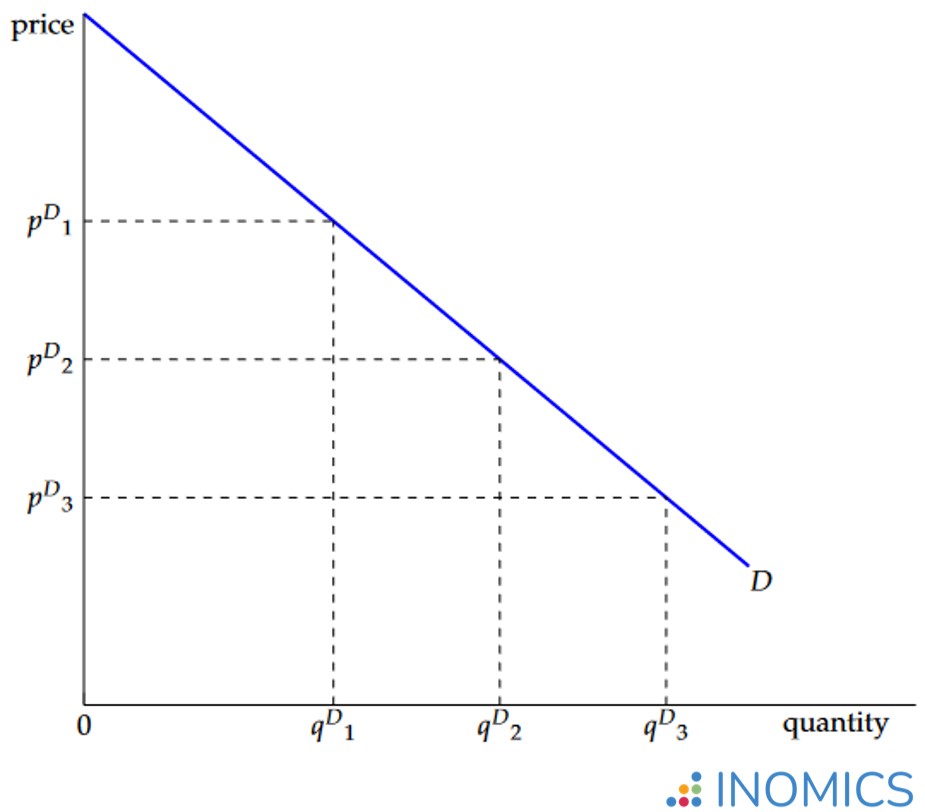
Source Image: inomics.com
Download Image
Phillips Curve in the Short & Long Run | Definition & Graph – Lesson | Study.com Hint Check Answer < Question 11 of 15 > Attempt 2 The graphs illustrate an initial equilibrium for the economy. Suppose that unexpectedly good weather causes a much larger yield of corn crops than expected. Use the graphs to show the new positions of aggregate demand (AD), short-run aggregate supply (SRAS), and This problem has been solved!

Source Image: study.com
Download Image
Germany: Reaching net zero while safeguarding social cohesion – ECOSCOPE In this example, our demand and supply model will illustrate the market for salmon in the year before the good weather conditions began—you can see it above. The demand curve D0 and the supply curve S0 show that the original equilibrium price was $3.25 per pound and the original equilibrium quantity was 250,000 fish. This price per

Source Image: oecdecoscope.blog
Download Image
Nominal GDP >>> Aggregate Demand – Econlib Shortrun equilibrium. An economy is in short-run equilibrium when the aggregate amount of output demanded is equal to the aggregate amount of output supplied. In the AD-AS model, you can find the short-run equilibrium by finding the point where AD intersects SRAS. The equilibrium consists of the equilibrium price level and the equilibrium output.
 Download Image
Download ImageTiny motion is measured by quantum squeezing and amplification – Physics World Next, consider how an economic change (e.g. a natural disaster, a change in production technology, a change in tastes and preferences, income, etc.) might affect supply or demand, then make adjustments to the graph to identify the new equilibrium point. Step 1. Draw demand and supply curves showing the market before the economic change took place.
Source Image: physicsworld.com
Download Image
Long Run Equilibrium of Competitive Firm and Industry A Decrease in Demand. Panel (b) of Figure 3.10 “Changes in Demand and Supply” shows that a decrease in demand shifts the demand curve to the left. The equilibrium price falls to $5 per pound. As the price falls to the new equilibrium level, the quantity supplied decreases to 20 million pounds of coffee per month.

Source Image: toppr.com
Download Image
Demand Curve | INOMICS
Long Run Equilibrium of Competitive Firm and Industry in a market setting, disequilibrium occurs when quantity supplied is not equal to the quantity demanded; when a market is experiencing a disequilibrium, there will be either a shortage or a surplus. equilibrium price. the price in a market at which the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied of a good are equal to one another; this is also
Germany: Reaching net zero while safeguarding social cohesion – ECOSCOPE Tiny motion is measured by quantum squeezing and amplification – Physics World Shortrun equilibrium. An economy is in short-run equilibrium when the aggregate amount of output demanded is equal to the aggregate amount of output supplied. In the AD-AS model, you can find the short-run equilibrium by finding the point where AD intersects SRAS. The equilibrium consists of the equilibrium price level and the equilibrium output.